Blog
flume-03 入门案例
监控端口数据
- 需求
使用Flume监听一个端口,收集该端口数据,并打印到控制台
- 分析
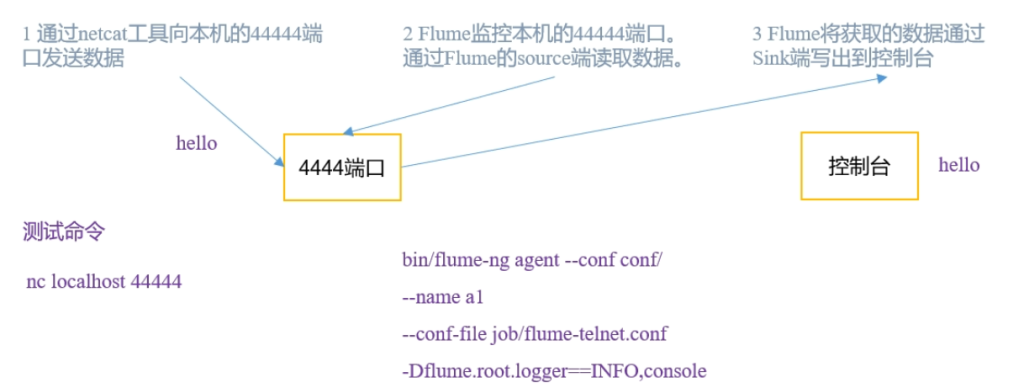
安装netcat
sudo yum install -y nc判断44444端口是否被占用
sudo netstat -tunlp | grep 44444nc开启服务端
nc -lk 44444nc开启客户端
nc localhost 44444创建flume agent配置文件 netcat-flume-logger.conf
# agent组件命名
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
# source组件配置
a1.sources.r1.type = netcat
a1.sources.r1.bind = localhost
a1.sources.r1.port = 44444
# sink组件配置
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger
# channel组件配置
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
# 缓冲容量1000个Event
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
# 传输速率 一次传多少
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# 组件关联
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
# 一个sink对应一个channel
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1启动命令
bin/flume-ng agent
--name a1
--conf conf
--conf-file jobs/netcat-flume-logger.conf
-Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
# 或者
bin/flume-ng agent -n a1 -c conf -f jobs/netcat-flume-logger.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console实时监控单个追加文件
- 需求
实时监控Hive日志,并上传到HDFS中
- 分析
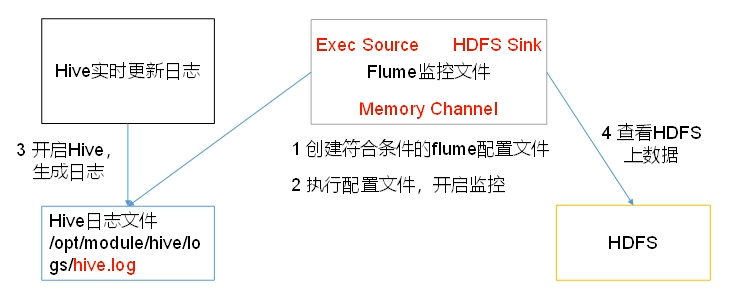
实现监控一个文件 并将结果打印到终端
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
a1.sources.r1.type = exec
# /home/test.log 监控文件路径
a1.sources.r1.command = tail -f /home/test.log
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1flume想要将数据传输到HDFS必须有Hadoop相关jar包

hadoop3只需要替换guava包
- 将flume/lib/guava-11.0.2.jar替换为hadoop3/share/hadoop/hdfs/lib/guava-27.0-jre.jar
以下三者满足其一即滚动文件,设置0则无视当前项规则
- hdfs.rollInterval
- 多久生成一个新的文件 单位秒
- hdfs.rollSize
- 134217700 设置每个文件的滚动大小,一般设置块大小 略小一点
- hdfs.rollCount
- 一般关闭设置0 文件滚动与Event数量无关
其他:
- hdfs.batchSize
- 积攒多少个Event才flush到HDFS一次
- hdfs.filePrefix
- log 上传文件的前缀
- hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp
- true 是否使用本地时间戳
- hdfs.fileType
- DataStream设置文件类型,可支持压缩
控制一天一个日志文件夹
- hdfs.round
- true 是否按照时间滚动文件夹
- hdfs.roundValue
- 1 多少时间单位创建一个新的文件夹
- hdfs.roundUnit
- hour 重新定义时间单位
提示:可以使用-Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console来查看写入过程是否出错
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
a1.sources.r1.type = exec
a1.sources.r1.command = tail -F /home/test.log
a1.sinks.k1.type = hdfs
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.path = hdfs://hadoop001:8020/flume/%Y%m%d/%H
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.filePrefix = log
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollInterval = 30
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollSize = 134217700
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollCount = 0
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.fileType = DataStream
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.round = true
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundValue = 1
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundUnit = hour
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp = true
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1实时监控目录下多个新文件
- 需求
使用Flume监听整个目录的文件,并上传至HDFS
- 分析
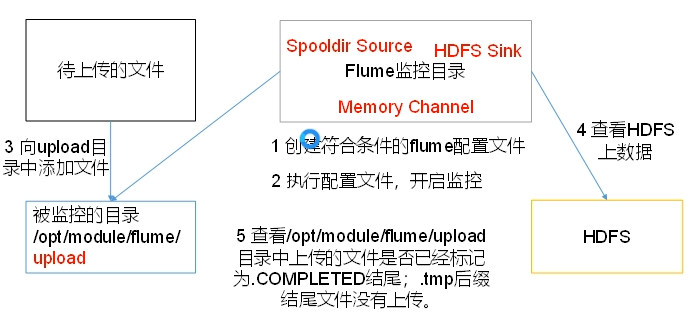
Spooldir是监控新文件,而不是有文件新增内容
- spoolDir监控的目标文件夹 默认500ms扫描一次文件夹
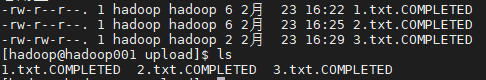
- fileSuffix已同步完毕文件添加后缀标识
- includePattern 正则
- ignorePattern 正则 不监控的文件
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
a1.sources.r1.type = spooldir
a1.sources.r1.spoolDir = /home/upload
a1.sinks.k1.type = hdfs
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.path = hdfs://hadoop001:8020/flume/%Y%m%d/%H
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.filePrefix = log
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollInterval = 30
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollSize = 134217700
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollCount = 0
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.fileType = DataStream
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.round = true
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundValue = 1
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundUnit = hour
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp = true
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1实时监控目录下的多个追加文件
exec source适用于监控一个实时追加的文件,但不能保证数据不丢失
spooldir source能保证数据不丢失,且能够实现断点续传,但延迟高,不能实时监控
taildir技能实现断点续传,又可以保证数据不丢失,还能够进行实时监控
- 需求
使用flume监听整个目录的实施追加文件,并上传至hdfs
- 分析
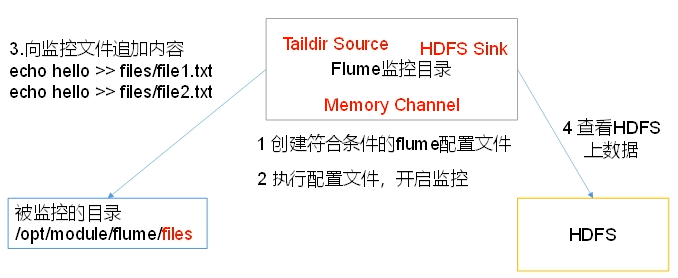
使用logger sink 方便查看
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
a1.sources.r1.type = TAILDIR
a1.sources.r1.filegroups = f1
a1.sources.r1.filegroups.f1 = /home/hadoop/test1/.*.txt
a1.sources.r1.positionFile = /home/hadoop/position/position.json
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1